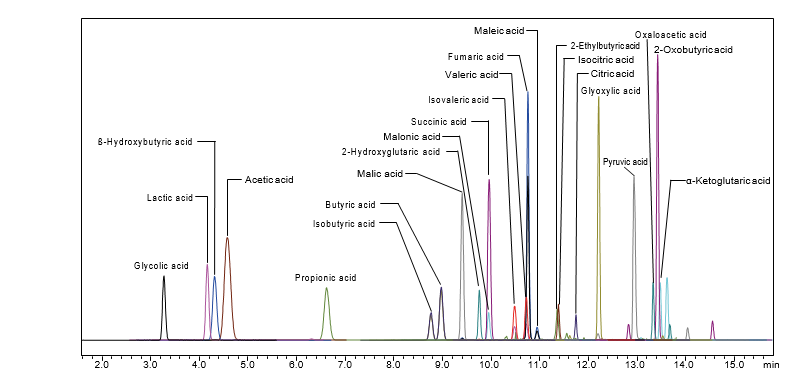
Of the short-chain fatty acids produced by intestinal bacteria, acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid are well known, and it has been reported that there are some connections between them and lifestyle-related diseases such as obesity and diabetes. Generally speaking, short-chain fatty acids are highly volatile and highly hydrophilic. This makes it difficult to perform LCMS analysis using a conventional reversed phase system. For that reason, this method package targets short-chain fatty acids (C2 to C5) that have been derivatized using 3-nitrophenylhydrazine (3-NPH). After setting MRM transitions, it can be used for the simultaneous analysis of 22 components, including organic acids related to the central metabolic pathways
| Short-Chain Fatty Acids | Organic Acids |
| Acetic acid | 2-oxobutyric acid |
| Propionic acid | 2-hydroxyglutaric acid |
| Butyric acid | α-ketoglutaric acid |
| Isobutyric acid | β-hydroxybutyric acid |
| Valeric acid | Isocitric acid |
| Isovaleric acid | Oxaloacetic acid |
| Citric acid | |
| Glyoxylic acid | |
| Glycolic acid | |
| Succinic acid | |
| Lactic acid | |
| Pyruvic acid | |
| Fumaric acid | |
| Maleic acid | |
| Malonic acid | |
| Malic acid |
The entire protocol necessary for pretreatment, including the derivatization step using 3-nitrophenylhydrazine, is contained in the Instruction Manual. By following these procedures, an analyst should be able to perform the entire process, from derivatization to data acquisition and data analysis, immediately after the package is introduced.